Types Of Pain
The pain experienced by animals during and after procedures differs, and therefore so does management of this pain.
Give Production Animals A Better Start With Long-Lasting Pain Management

Effective Pain Relief For Lambs And Calves
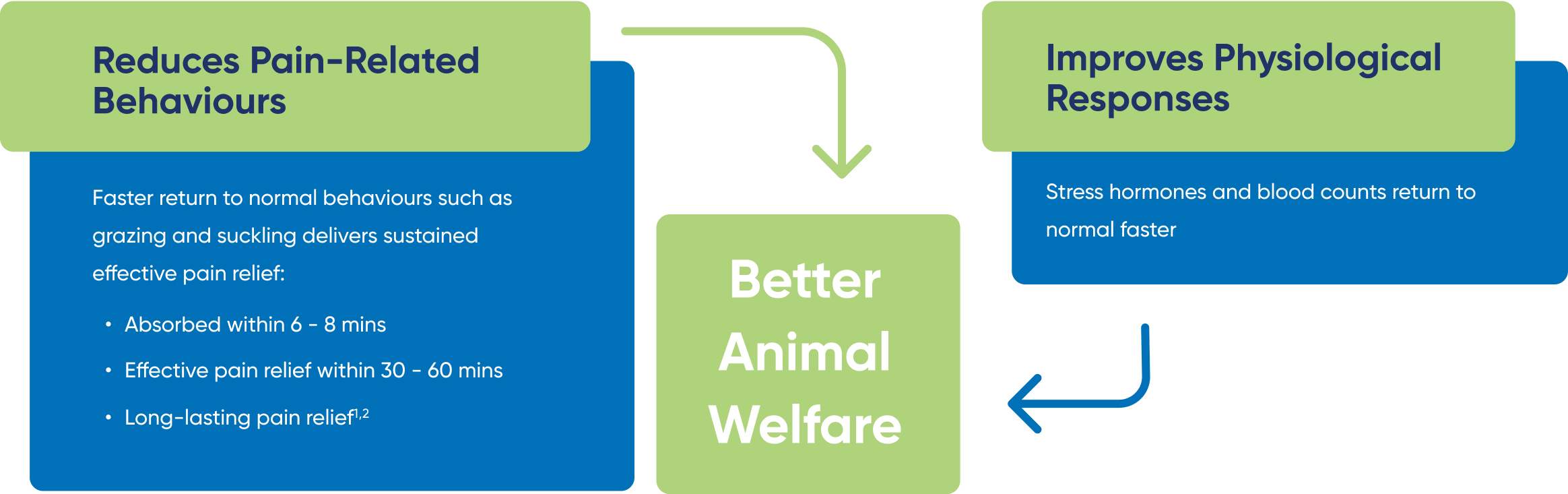
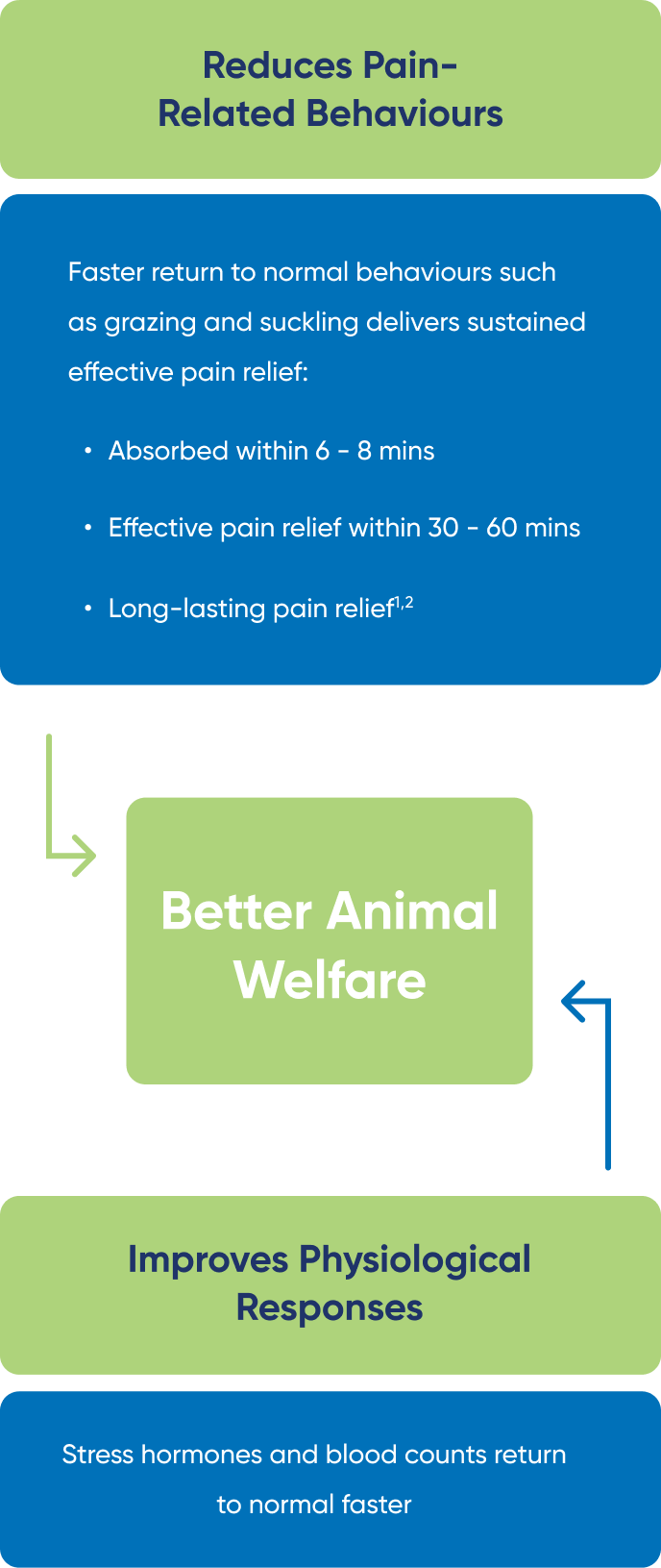
BUTEC OTM has been shown to result in treated animals displaying less pain-related behaviours and displaying more normal activities such as grazing, rumination, suckling, and lying down relative to untreated animals following surgical husbandry procedures.
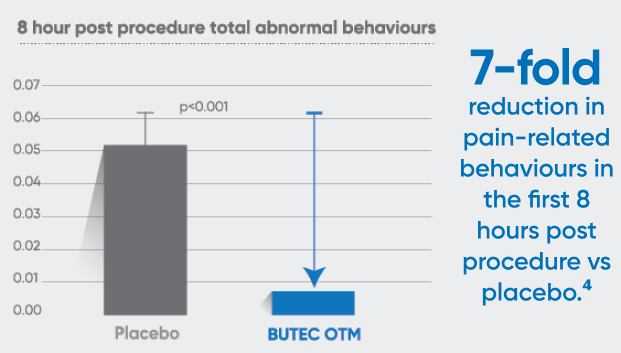
Castration And Tail Docking In Lambs
Merino lambs (n = 60) aged 7 – 10 weeks underwent knife castration and hot-iron tail docking. Lambs were randomly allocated to either a placebo group or BUTEC OTM treatment group.
Observations were carried out every 15 minutes for the first 8 hours post procedure and then 3 observation periods, 15 minutes apart, were carried out 24 hours post procedure. Observers were blinded to whether the lambs were treated with BUTEC OTM or placebo.
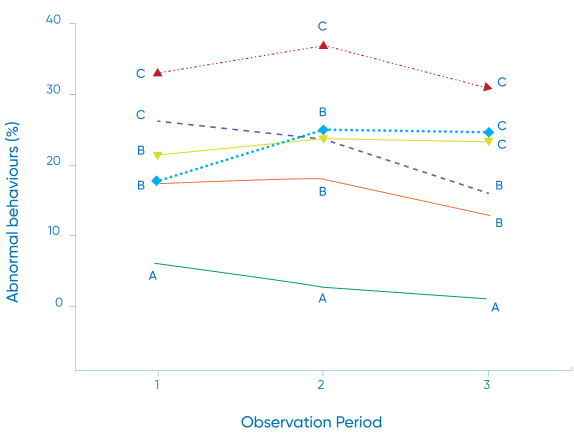
Mulesing In Lambs
120 female lambs aged 6 — 10 weeks underwent surgical mulesing and tail docking. Lambs were ranked according to body weight and then randomly allocated to treatment groups. They were observed at time intervals post-procedure by observers who were blinded to any treatments given to the lambs.
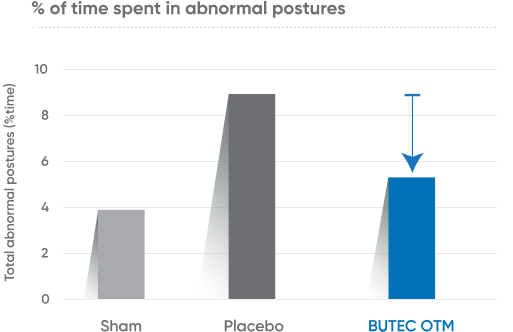
Surgical Castration In Calves
Surgical castration was carried out on 40 cross-bred bull calves (9 — 11 weeks old). Pain-related behaviours were assessed every 5 minutes in the first hour post castration. Postural behaviours were classified every 15 minutes for 8 hours post castration and again for 4 hours on the following day.